Advantages of the silo bag
The silo bag offers high-quality grain storage at a minimal cost:
The grain is kept in anaerobic conditions, free from insects and fungi, preserving its quality and reducing transportation costs.
Grain Storage in Silo Bags
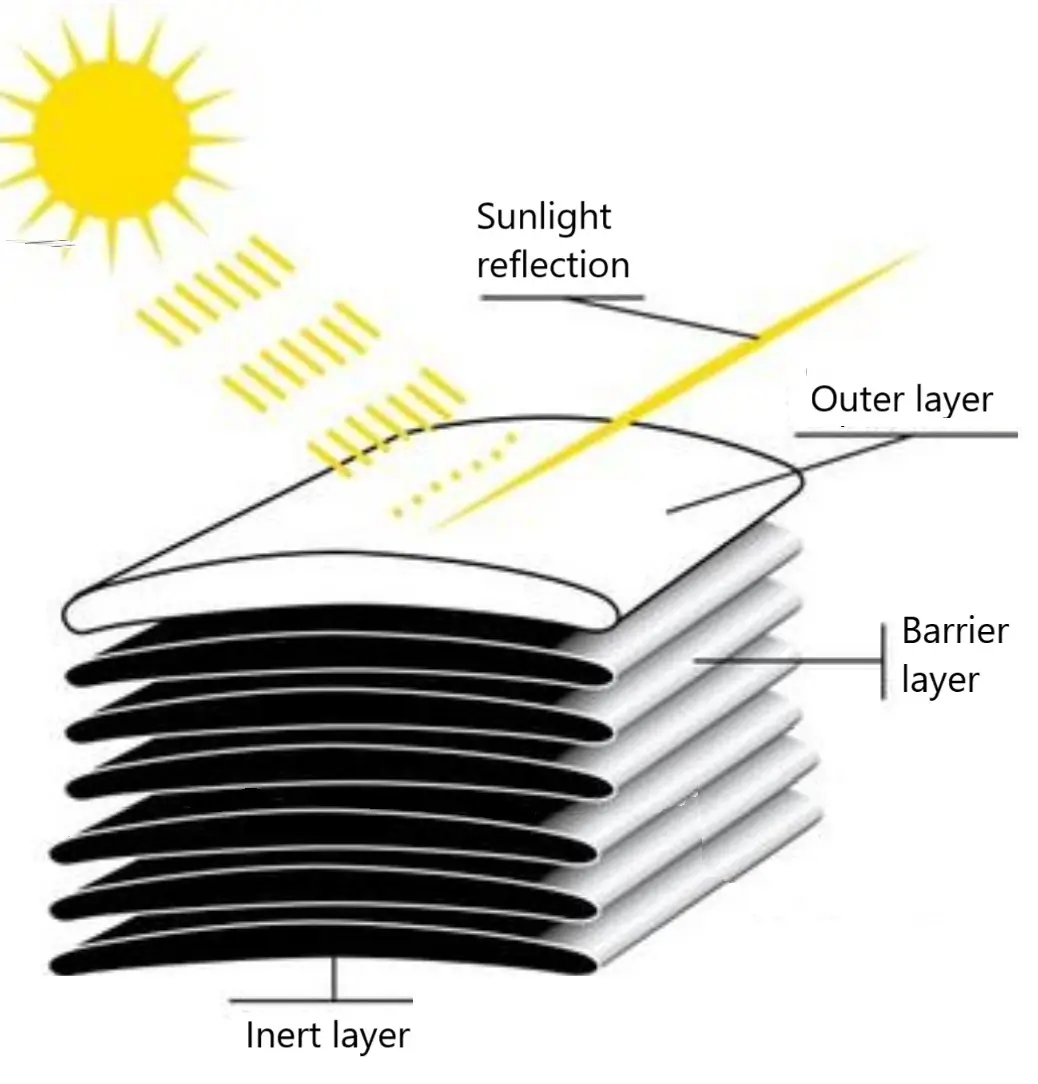
In the late 1990s, Argentina adapted the use of silo bags for storing dry grain, a technology now widely used for storing corn, wheat, soybeans, and sunflower. These silos are also suitable for other crops such as barley, canola, and beans. While their use is still limited in countries like Russia, Ukraine, and Kazakhstan, silo bags offer significant advantages: grain is bagged, hermetically sealed, and the anaerobic environment eliminates insects, fungi, and bacteria, preserving product quality without allowing oxygen, moisture, or sunlight to enter.
Challenges of Traditional Grain Storage Structures
Traditional structures such as fixed elevators, warehouses, and granaries have been standard methods for grain storage for decades. However, their construction and maintenance involve high costs, limiting their availability, especially for small or medium-sized producers. Additionally, these facilities have fixed capacities that cannot easily adjust to exceptional yields, leading to challenges during abundant harvests.
Another key aspect is the maintenance and quality control of stored grain. Grain elevators, for example, require regular inspections and constant quality checks of the processed product. These processes increase operating costs and impact profitability when marketing the grain.
The Silo Bag: A Flexible and Cost-Effective Alternative The silo bag stands out as a modern and accessible solution for grain storage, eliminating the
for large infrastructure investments. Without requiring construction or maintenance of fixed facilities, initial costs are significantly reduced, making this technology more accessible to all producers.
Moreover, silo bags excel in flexibility. Their capacity can easily adjust to crop yields; in the case of higher yields, the solution is as simple as increasing the number of bags used, offering a significant advantage over the limitations of traditional methods.
Transportation Optimization and Cost Reduction
During harvest, the high demand for transportation to traditional silos creates bottlenecks and increases logistical costs. The silo bag eliminates this issue by allowing grain to be stored directly in the field, reducing pressure on transportation systems.
Additionally, this technology enables better planning for grain transport. By storing in silo bags, producers have the flexibility to hire transportation during periods of lower demand, obtaining more competitive prices and improving economic efficiency.
Silo Bag Alternatives Are:
For Producers:
8 or 9 feet with lengths of 60 m, 75 m, or 100 m, and thicknesses of 225 µm (Silage) and 270 µm (Grain Storage).
For Collectors:
10 or 12 feet with lengths of 60 m, 75 m, and thicknesses of 225 µm (Silage) and 270 µm (Grain Storage).
A seven-layer silo bag measuring 9 feet x 60 m can store up to 225 tons.
A seven-layer silo bag measuring 9 feet x 75 m can store up to 255 tons.








